Fully automatic non-interactive application for HTTPS certificate

Preface
What is HTTP/HTTPS?
To put it simply, HTTP is a protocol for transmitting web page content. For example, when we browse a web page, the text, pictures, CSS, JS and other files on the web page are all transmitted to our browser through the HTTP protocol, and then we can see it. Because HTTP is transmitted in clear text, the content transmitted through the HTTP protocol is easy to be peeped and tampered with. For security (you definitely don’t want to be peeked or tampered with the content of the webpage, such as the website bank password or something.) Then for the HTTP protocol Added a layer of SSL/TLS security protocol, so there is HTTPS.
What is SSL/TLS?
SSL refers to Secure Sockets Layer (Secure Sockets Layer). Students with a pure heart can also understand it as "HTTP with a condom". Because of the condom, it is of course safer. TLS is a Transport Layer Security protocol (Transport Layer Security). SSL and TLS are different stages of the same thing. It can be understood as the same thing, as long as they are both security protocols.
Why deploy HTTPS?
After all, HTTPS is more secure. Even for security, a professional and reliable website, HTTPS is a must. Both Firefox and Chrome plan to mark HTTP websites that do not configure SSL encryption as insecure, and they are currently working with other related foundations and companies to promote the HTTPSization of the entire Internet, and some of the major websites that everyone visits now. For example, Google has fully enabled HTTPS many years ago, and domestic Taobao, Sogou, Zhihu, Baidu, etc. have also fully enabled HTTPS. Even Google and Baidu's search results are giving higher rankings and priority to HTTPS websites.
How to deploy HTTPS?
You only need to have an SSL security certificate issued by a trusted CA (Certificate Authority), that is, a certificate authority, and deploy it on your website server. Once the deployment is successful, when the user visits your website, the browser will add a small green lock in front of the URL displayed, indicating that the website is safe. Of course, you will also see that the prefix in front of the URL has changed to HTTPS , no longer HTTP.
How to get SSL security certificate?
In theory, we can also issue SSL security certificates ourselves, but the security certificates we issue ourselves will not be trusted by mainstream browsers, so we need security certificates issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA). The general SSL security certificate issuance services are relatively expensive. For example, certificates issued by Godaddy, GlobalSign and other organizations generally cost $20 a year or more. However, in order to accelerate the popularization of HTTPS, EEF Electronic Frontier Foundation, Mozilla Foundation and The University of Michigan established a non-profit organization called ISRG (Internet Security Research Group), which has launched Let's Encrypt free certificates since 2015. This free certificate is not only free, but also quite easy to use, so we can use the free certificate provided by Let’s Encrypt to deploy HTTPS.
Introduction to Let’s Encrypt
As mentioned earlier, Let’s Encrypt is a free security certificate program launched by an organization called ISRG (Internet Security Research Group, Internet Security Research Group). The organizations and companies participating in this plan can be said to be the most important pioneers of the Internet. In addition to the three aggressive initiators mentioned above, Cisco (the leader of the global network equipment manufacturer), Akamai, and even Even the Linux Foundation has joined the cooperation, and the participation of these big-name organizations ensures the credibility and sustainability of this project.
Introduction to Certbot
EFF (Electronic Frontier Foundation), the initiator of ISRG, released an official client Certbot for the Let’s Encrypt project, which can be used to fully automate the acquisition, deployment and renewal of security certificates. Although third-party tools can also be used, official tools are more authoritative, less risky, and easier to solve problems encountered, after all, there is official support.
Weak interaction application process
According to the conventional certbot application process, you need to fill in the email address, and you need to go to the DNS server to set the corresponding TXT according to the process prompts. Although it is not complicated, it is cumbersome for lazy people to do one more step. Du Niang took a moment and found that some experts have already solved this problem. It turns out that people who are lazy than you are smarter than you.
The specific steps are as follows: (Source: https://github.com/ywdblog/certbot-letsencrypt-wildcardcertificates-alydns-au)
1. Download
git clone https://github.com/ywdblog/certbot-letsencrypt-wildcardcertificates-alydns-au
cd certbot-letsencrypt-wildcardcertificates-alydns-au
chmod 0777 au.sh
2. Configuration
2.1. DNS API Key
What does this API key mean? Since the records of Alibaba Cloud DNS or Tencent Cloud DNS need to be operated through the API, it is necessary to obtain the API key from the domain name service provider, and then configure it in the au.sh file:
ALY_KEY and ALY_TOKEN: Alibaba Cloud API key and Secret official application documents.
TXY_KEY and TXY_TOKEN: Tencent Cloud API key official application documents.
GODADDY_KEY and GODADDY_TOKEN: GoDaddy API key official application documents.
2.2 Select the operating environment
Currently, the tool supports five operating environments and scenarios, which are invoked through hook files and parameters:
PHP (>4 and above versions are acceptable)
au.sh php aly add/clean: Indicates selecting the PHP command line, operating Alibaba Cloud DNS, and adding/clearing DNS.au.sh php txy add/clean: Indicates selecting the PHP command line, operating Tencent Cloud DNS, and adding/clearing DNS.au.sh php godaddy add/clean: Indicates selecting the PHP command line, operating GoDaddy DNS, and adding/clearing DNS.
Python (versions 2.7 and 3.7 are supported)
au.sh python aly add/clean: Indicates selecting the Python command line, operating Alibaba Cloud DNS, and adding/clearing DNS.au.sh python txy add/clean: Indicates selecting the Python command line, operating Tencent Cloud DNS, and adding/clearing DNS. (Need to install third-party libraries, pip install requests or pip3 install requests, I will optimize the use of python built-in libraries later)
Choose any hook shell (including corresponding parameters) according to your server environment and domain name service provider. See below for specific usage.
2.3 Apply for a certificate
Test for errors:
./certbot-auto certonly -d *.example.com --manual --preferred-challenges dns --dry-run --manual-auth-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly add" --manual- cleanup-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
Debug: You may encounter a series of problems when operating the DNS API, such as insufficient API token permissions. If you encounter related problems, you can check /var/log/certd.log.
Important Explanation: --manual-auth-hook and --manual-cleanup-hook have three parameters:
The first one represents the language you want to choose (php/python)
The second parameter represents your DNS vendor (aly/txy)
The third parameter is fixed (use add in --manual-auth-hook, use clean in --manual-clean-hook)
For example, if you want to choose a Python environment, you can change the --manual-auth-hook input to "/script directory/au.sh python aly add", --manual-cleanup-hook input to "/script directory/au.sh python aly clean"
After confirming that it is correct, actually run it (remove the --dry-run parameter):
# actual application
./certbot-auto certonly -d *.example.com --manual --preferred-challenges dns --manual-auth-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly add" --manual-cleanup-hook "/ script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
Parameter explanation (you don't need to care about it):
certonly: Indicates that the verification mode is adopted, only the certificate will be obtained, and the certificate will not be configured for the web server
--manual: Indicates the plugin
--preferred-challenges dns: Indicates that DNS is used to verify the legitimacy of the applicant (whether it is the manager of the domain name)
--dry-run: test before actually applying for/renewing the certificate, strongly recommended
-d: Indicates that you need to apply for a certificate for that domain name, there can be more than one.
--manual-auth-hook: call a hook file when executing the command
--manual-cleanup-hook: Clear DNS added records
If you want to apply for a wildcard certificate for multiple domain names (combined into one certificate, also called SAN wildcard certificate), just enter multiple -d parameters directly, for example:
./certbot-auto certonly -d *.example.com -d *.example.org -d www.example.cn --manual --preferred-challenges dns --dry-run --manual-auth-hook "/ script directory/au.sh php aly add" --manual-cleanup-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
Renew Certificate
1. Renew all certificates on the machine
./certbot-auto renew --manual --preferred-challenges dns --manual-auth-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly add" --manual-cleanup-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
2. Renew a certificate
First look at how many certificates are on the machine:
./certbot-auto certificates
You can see many certificates, as shown in the figure:
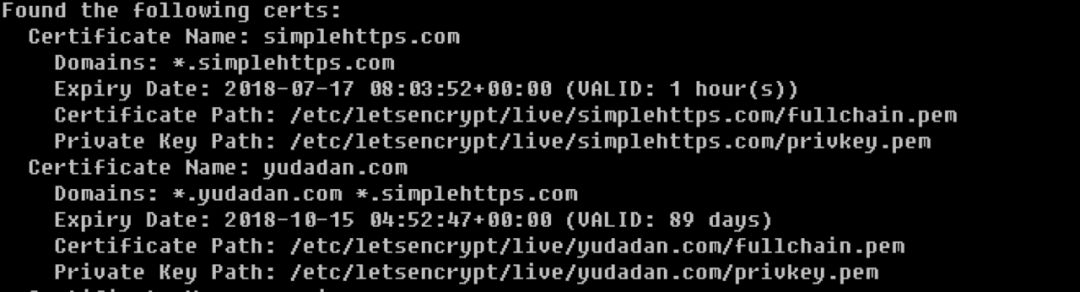
Remember the certificate name, such as simplehttps.com, and run the following command to renew:
./certbot-auto renew --cert-name simplehttps.com --manual-auth-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly add" --manual-cleanup-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
Join crontab
Edit the file /etc/crontab :
#Certificate validity period < 30 days will be renewed, so crontab can be configured as 1 day or 1 week
1 1 */1 * * root certbot-auto renew --manual --preferred-challenges dns --manual-auth-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly add" --manual-cleanup-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
If the certbot machine is the same as the machine running web services (such as nginx, apache), then after successfully renewing the certificate, you can start the corresponding web server and run the following crontab:
# Note that nginx will only be restarted if the certificate is successfully renew
1 1 */1 * * root certbot-auto renew --manual --preferred-challenges dns -deploy-hook "service nginx restart" --manual-auth-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly add" - -manual-cleanup-hook "/script directory/au.sh php aly clean"
Note: Only a single machine is recommended to run in this way. If you want to synchronize the certificate to multiple web servers, you need another solution.
No interactive application process
Although I can already save the operation steps of going to the DNS server to modify the TXT record, I have been lazy for a while, but I still have to enter an email address and answer a few questions that I don’t care about at all, which is really tasteless. Later, I checked the official documentation of certbot. In fact, they have done a very perfect job and absolutely support this kind of operation. Just add three parameters --non-interactive --agree-tos --register-unsafely-without-email Realize full automation. Finally, the script is optimized and placed on the server. Just execute a command to automatically register the HTTPS certificate.
curl -s -S -L https://install.wydiy.com/shell/https_install.sh | bash -s "mydomain.com" aly apikey apitoken
Among them, mydomain.com is the domain name, aly is the cloud platform, including txy and gdd, apikey and apitoken can be found on the cloud platform.